Foreword
看一下如何写一个MCP服务
FastMCP
翻了一下看到了MCP有一个快速的模式,这种方式不需要写那么多前置代码
# server.py
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Create an MCP server
mcp = FastMCP("Demo")
# 通过注解快速加入一个工具命令
# Add an addition tool
@mcp.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers"""
return a + b
# 这里还通过注解,加入了有一部分资源
# 这里的资源可以理解为一个文件或者一段信息,或者说一个特定的内容,这个可以给LLM去获取的
# Add a dynamic greeting resource
@mcp.resource("greeting://{name}")
def get_greeting(name: str) -> str:
"""Get a personalized greeting"""
return f"Hello, {name}!"
快速安装,启动服务
mcp install server.py
mcp dev server.py
这种方式更接近于你提前告诉了LLM你有一个函数,他的输入输出模式是什么样的,调用起来稍微有点死板
除了工具和资源注解,还有一个prompt的注解,其实就是现在ChatGPT里的各种角色扮演的prompt,只是内置到了mcp里而已
@mcp.prompt()
Git MCP Server
https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/servers/tree/main/src/git
先看Git的MCP Server,主要是用python写的
import click
from pathlib import Path
import logging
import sys
from .server import serve
@click.command()
@click.option("--repository", "-r", type=Path, help="Git repository path")
@click.option("-v", "--verbose", count=True)
def main(repository: Path | None, verbose: bool) -> None:
"""MCP Git Server - Git functionality for MCP"""
import asyncio
logging_level = logging.WARN
if verbose == 1:
logging_level = logging.INFO
elif verbose >= 2:
logging_level = logging.DEBUG
logging.basicConfig(level=logging_level, stream=sys.stderr)
asyncio.run(serve(repository))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
这里主要是支持通过命令行调用工具,启动一个git仓库的管理服务
主要git仓库的实现是看这里的server.py
import logging
from pathlib import Path
# 接口数据类型显式定义模块
from typing import Sequence
# 这里主要是mcp相关的server接口定义
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.server.session import ServerSession
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
from mcp.types import (
ClientCapabilities,
TextContent,
Tool,
ListRootsResult,
RootsCapability,
)
from enum import Enum
# 主要是依赖git模块实现git操作
import git
# 基础的数据验证模块
from pydantic import BaseModel
# 这里主要是对各个命令的参数基类进行定义
class GitStatus(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
class GitDiffUnstaged(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
class GitDiffStaged(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
class GitDiff(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
target: str
class GitCommit(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
message: str
class GitAdd(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
files: list[str]
class GitReset(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
class GitLog(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
max_count: int = 10
class GitCreateBranch(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
branch_name: str
base_branch: str | None = None
class GitCheckout(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
branch_name: str
class GitShow(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
revision: str
class GitInit(BaseModel):
repo_path: str
# 这里定义工具类本身
class GitTools(str, Enum):
STATUS = "git_status"
DIFF_UNSTAGED = "git_diff_unstaged"
DIFF_STAGED = "git_diff_staged"
DIFF = "git_diff"
COMMIT = "git_commit"
ADD = "git_add"
RESET = "git_reset"
LOG = "git_log"
CREATE_BRANCH = "git_create_branch"
CHECKOUT = "git_checkout"
SHOW = "git_show"
INIT = "git_init"
# 这里是各个函数的具体实现
def git_status(repo: git.Repo) -> str:
return repo.git.status()
def git_diff_unstaged(repo: git.Repo) -> str:
return repo.git.diff()
def git_diff_staged(repo: git.Repo) -> str:
return repo.git.diff("--cached")
def git_diff(repo: git.Repo, target: str) -> str:
return repo.git.diff(target)
def git_commit(repo: git.Repo, message: str) -> str:
commit = repo.index.commit(message)
return f"Changes committed successfully with hash {commit.hexsha}"
def git_add(repo: git.Repo, files: list[str]) -> str:
repo.index.add(files)
return "Files staged successfully"
def git_reset(repo: git.Repo) -> str:
repo.index.reset()
return "All staged changes reset"
def git_log(repo: git.Repo, max_count: int = 10) -> list[str]:
commits = list(repo.iter_commits(max_count=max_count))
log = []
for commit in commits:
log.append(
f"Commit: {commit.hexsha}\n"
f"Author: {commit.author}\n"
f"Date: {commit.authored_datetime}\n"
f"Message: {commit.message}\n"
)
return log
def git_create_branch(repo: git.Repo, branch_name: str, base_branch: str | None = None) -> str:
if base_branch:
base = repo.refs[base_branch]
else:
base = repo.active_branch
repo.create_head(branch_name, base)
return f"Created branch '{branch_name}' from '{base.name}'"
def git_checkout(repo: git.Repo, branch_name: str) -> str:
repo.git.checkout(branch_name)
return f"Switched to branch '{branch_name}'"
def git_init(repo_path: str) -> str:
try:
repo = git.Repo.init(path=repo_path, mkdir=True)
return f"Initialized empty Git repository in {repo.git_dir}"
except Exception as e:
return f"Error initializing repository: {str(e)}"
def git_show(repo: git.Repo, revision: str) -> str:
commit = repo.commit(revision)
output = [
f"Commit: {commit.hexsha}\n"
f"Author: {commit.author}\n"
f"Date: {commit.authored_datetime}\n"
f"Message: {commit.message}\n"
]
if commit.parents:
parent = commit.parents[0]
diff = parent.diff(commit, create_patch=True)
else:
diff = commit.diff(git.NULL_TREE, create_patch=True)
for d in diff:
output.append(f"\n--- {d.a_path}\n+++ {d.b_path}\n")
output.append(d.diff.decode('utf-8'))
return "".join(output)
下面是具体的serve实现
async def serve(repository: Path | None) -> None:
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
if repository is not None:
try:
# 对git进行初始化
git.Repo(repository)
logger.info(f"Using repository at {repository}")
except git.InvalidGitRepositoryError:
logger.error(f"{repository} is not a valid Git repository")
return
# 注册服务
server = Server("mcp-git")
# 通过注解绑定对应的功能
@server.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> list[Tool]:
return [
# AI能理解这个功能是干啥的,主要就是靠这个description了
Tool(
name=GitTools.STATUS,
description="Shows the working tree status",
inputSchema=GitStatus.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.DIFF_UNSTAGED,
description="Shows changes in the working directory that are not yet staged",
inputSchema=GitDiffUnstaged.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.DIFF_STAGED,
description="Shows changes that are staged for commit",
inputSchema=GitDiffStaged.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.DIFF,
description="Shows differences between branches or commits",
inputSchema=GitDiff.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.COMMIT,
description="Records changes to the repository",
inputSchema=GitCommit.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.ADD,
description="Adds file contents to the staging area",
inputSchema=GitAdd.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.RESET,
description="Unstages all staged changes",
inputSchema=GitReset.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.LOG,
description="Shows the commit logs",
inputSchema=GitLog.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.CREATE_BRANCH,
description="Creates a new branch from an optional base branch",
inputSchema=GitCreateBranch.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.CHECKOUT,
description="Switches branches",
inputSchema=GitCheckout.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.SHOW,
description="Shows the contents of a commit",
inputSchema=GitShow.schema(),
),
Tool(
name=GitTools.INIT,
description="Initialize a new Git repository",
inputSchema=GitInit.schema(),
)
]
# 这里主要是获取当前目录下仓库列表,比如带有子仓库等,就会显示多个
async def list_repos() -> Sequence[str]:
async def by_roots() -> Sequence[str]:
if not isinstance(server.request_context.session, ServerSession):
raise TypeError("server.request_context.session must be a ServerSession")
if not server.request_context.session.check_client_capability(
ClientCapabilities(roots=RootsCapability())
):
return []
roots_result: ListRootsResult = await server.request_context.session.list_roots()
logger.debug(f"Roots result: {roots_result}")
repo_paths = []
for root in roots_result.roots:
path = root.uri.path
try:
git.Repo(path)
repo_paths.append(str(path))
except git.InvalidGitRepositoryError:
pass
return repo_paths
def by_commandline() -> Sequence[str]:
return [str(repository)] if repository is not None else []
cmd_repos = by_commandline()
root_repos = await by_roots()
return [*root_repos, *cmd_repos]
# 通过call_tool的注解来调用每个接口
@server.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
repo_path = Path(arguments["repo_path"])
# name就是具体调用的函数,arguements就是这个操作的参数字典
# 如果是仓库初始化,是不需要一个具体仓库对象的,所以直接操作就行了
# Handle git init separately since it doesn't require an existing repo
if name == GitTools.INIT:
result = git_init(str(repo_path))
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=result
)]
# 其他命令就需要一个具体的仓库对象
# For all other commands, we need an existing repo
repo = git.Repo(repo_path)
# 通过命令名字调用各个实现
match name:
case GitTools.STATUS:
status = git_status(repo)
# 具体的返回格式,就是这样约定的
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"Repository status:\n{status}"
)]
case GitTools.DIFF_UNSTAGED:
diff = git_diff_unstaged(repo)
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"Unstaged changes:\n{diff}"
)]
case GitTools.DIFF_STAGED:
diff = git_diff_staged(repo)
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"Staged changes:\n{diff}"
)]
case GitTools.DIFF:
diff = git_diff(repo, arguments["target"])
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"Diff with {arguments['target']}:\n{diff}"
)]
case GitTools.COMMIT:
result = git_commit(repo, arguments["message"])
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=result
)]
case GitTools.ADD:
result = git_add(repo, arguments["files"])
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=result
)]
case GitTools.RESET:
result = git_reset(repo)
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=result
)]
case GitTools.LOG:
log = git_log(repo, arguments.get("max_count", 10))
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text="Commit history:\n" + "\n".join(log)
)]
case GitTools.CREATE_BRANCH:
result = git_create_branch(
repo,
arguments["branch_name"],
arguments.get("base_branch")
)
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=result
)]
case GitTools.CHECKOUT:
result = git_checkout(repo, arguments["branch_name"])
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=result
)]
case GitTools.SHOW:
result = git_show(repo, arguments["revision"])
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=result
)]
case _:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown tool: {name}")
# 服务器初始化
options = server.create_initialization_options()
#
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.run(read_stream, write_stream, options, raise_exceptions=True)
看起来结构还是比较清晰的
async def serve(repository: Path | None) -> None:
# 注册能力
async def list_tools() -> list[Tool]:
...
# 调用能力
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
...
# 启动服务
options = server.create_initialization_options()
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.run(read_stream, write_stream, options, raise_exceptions=True)
Filesystem MCP Server
https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/servers/tree/main/src/filesystem
有了上面的python的基础,再看Filesystem MCP Server是用nodejs实现的,虽然是ts代码,但是总体逻辑一样的
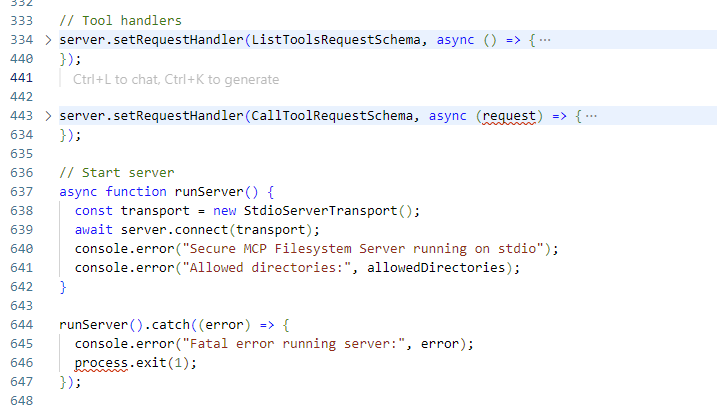
Summary
MCP Server内容大概是这些,后续可能随着发展这个还会有所变化
Quote
https://github.com/liaokongVFX/MCP-Chinese-Getting-Started-Guide
https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/python-sdk?tab=readme-ov-file#quickstart