41.Valid Sudoku
Determine if a Sudoku is valid, according to: Sudoku Puzzles - The Rules.
The Sudoku board could be partially filled, where empty cells are filled with the character ‘.’.
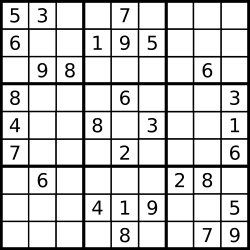
A partially filled sudoku which is valid.
Note: A valid Sudoku board (partially filled) is not necessarily solvable. Only the filled cells need to be validated.
41.Valid Sudoku-Analysis
验证是否是有效的数独。
题目要求不高,因为存在空的情况,所以他只要求验证当前的数独是否合乎规则,而不用去验证是否有解,计算解
所以只需要检验,每一行,每一列,以及每个小九宫格中不出现重复的数字就是ok的
41.Valid Sudoku-Solution-C/C++
除了比较复杂再就没什么了
bool isValidSudoku(char** board, int boardRowSize, int boardColSize)
{
int i=0,j=0,k=0,n=0,f;
int num[9]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
//以i做横行检测
for(j=0;j<9;j++)
{
if(board[i][j]!='.')
num[board[i][j]-49]++;
}
for(k=0;k<9;k++)
{
if(num[k]>1)
return false;
else
num[k]=0;
}
}
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
//以i做竖列检测
for(j=0;j<9;j++)
{
if(board[j][i]!='.')
num[board[j][i]-49]++;
}
for(k=0;k<9;k++)
{
if(num[k]>1)
return false;
else
num[k]=0;
}
}
//小九宫格检测
for(k=0;k<9;k=k+3)
for(n=0;n<9;n=n+3)
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
//以i做竖列检测
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if(board[k+i][j+n]!='.')
num[board[k+i][j+n]-49]++;
//printf("%c",board[k+i][j+n]);
}
}
for(f=0;f<9;f++)
{
if(num[f]>1)
return false;
else
num[f]=0;
}
//printf("%d %d ",k+i,j+n);
}
return true;
}
41.Valid Sudoku-Solution-Python
Python用另外一种方法,每检测一个格子,就在所在行、列、小九宫格内进行一次检查,查找是否有重复的元素,只要找到了,就返回false 否则就继续寻找直到结束
在这里还发现了一个东西,python可以在函数里定义函数,这样就很方便啊,只为某一个特定目的而写的函数,不需要要放到类中去,只需要存在与使用它的函数自身之中就可以了,是个不错的机制
class Solution(object):
def isValidSudoku(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:rtype: bool
"""
def isValid(x, y, tmp):
for i in range(9):
if board[i][y]==tmp:return False
for i in range(9):
if board[x][i]==tmp:return False
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if board[(x/3)*3+i][(y/3)*3+j]==tmp: return False
return True
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
if board[i][j]=='.':
continue
tmp=board[i][j]
board[i][j]='D'
if isValid(i,j,tmp)==False:
return False
else:
board[i][j]=tmp
return True
42.Length of Last Word
Given a string s consists of upper/lower-case alphabets and empty space characters ‘ ‘, return the length of last word in the string.
If the last word does not exist, return 0.
Note: A word is defined as a character sequence consists of non-space characters only.
For example,
Given s = “Hello World”,
return 5.
42.Length of Last Word-Analysis
返回最后一个单词的长度,单词的定义就是左右是空格 中间的是长度
所以只要顺序查找,如果找到尾部就结束
如果找到不为空格,那么找到了word,然后开始记录,如果找到下一个空格就结束
直到最后,但是这样有一个小问题,就是从头开始找到,因为想找的是最后一个word,所以其实比较慢。
42.Length of Last Word-Solution-C/C++
int lengthOfLastWord(char* s)
{
char* temp=s;
bool find=false;
int len=0;
while((*temp)!='\0')
{
if((*temp)==' '&& find)
{
find=false;
temp++;
continue;
}
if((*temp)!=' '&&(!find))
{
len=1;
find=true;
temp++;
continue;
}
if(find)
len++;
temp++;
}
return len;
}
42.Length of Last Word-Solution-Python
python的代码从尾部开始计算,首先把尾部的空格全部排除掉
然后从尾部开始找空格,找到空格就返回长度就行了。
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLastWord(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
spacelen=0
#首先判断尾部是否存在空格(包括连续空格)
if len(s)==0:
return 0
if s[-1]==' ':
for i in range(0,len(s)):
if s[len(s)-1-i]==' ':
spacelen=spacelen+1
else:
break;
slen=0
for i in range(0,len(s)-spacelen):
if s[len(s)-1-spacelen-i]!=' ':
slen=slen+1
continue
else:
return slen
return slen
43.Contains Duplicate II
Given an array of integers and an integer k, find out whether there are two distinct indices i and j in the array such that nums[i] = nums[j] and the difference between i and j is at most k.
43.Contains Duplicate II-Analysis
找数组中是否有两个重复元素并且重复元素间隔为小于等于k
依次遍历,在k的范围内搜索是否有和当前值相等的数,有就返回
没有就算了
但是也需要注意给定的搜索范围,越界的情况
所以随着搜索到最后阶段的时候需要不断减小搜索的范围来适应边界
43.Contains Duplicate II-Solution-C/C++
bool containsNearbyDuplicate(int* nums, int numsSize, int k)
{
int i=0,j=0,n=k;
for(i=0;i<numsSize-1;i++)
{
if(i+n>=numsSize)
n=numsSize-i;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(nums[i]==nums[i+j])
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
43.Contains Duplicate II-Solution-Python
理论上python的代码是正确的,但是超时了
查看了一下c的用时是1800多ms 想都不用想python肯定超过了2s
class Solution(object):
def containsNearbyDuplicate(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: bool
"""
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if i+k>=len(nums):
k=len(nums)-i
for j in range(1,k):
if nums[i]==nums[i+j]:
return True
return False;
用字典来做一个index和值的映射,然后通过每次插入前的检查,查看是否存在有在k范围内值,如果存在的话,就直接返回了。否则继续查找
class Solution:
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: bool
"""
def containsNearbyDuplicate(self, nums, k):
numDict = dict()
for x in range(len(nums)):
#从字典中搜索是否存在nums[x] 不存在会返回None 否则返回对应的值
idx = numDict.get(nums[x])
if idx >= 0 and x - idx <= k:
return True
numDict[nums[x]] = x
#把当前值和顺序x两个映射起来 存入字典中
return False
除了这种方法还有一种,用set的方法,每k个值存一次,然后看是否set的size和k相等,不相等就表示有重复内容
44.Rectangle Area
Find the total area covered by two rectilinear rectangles in a 2D plane.
Each rectangle is defined by its bottom left corner and top right corner as shown in the figure.
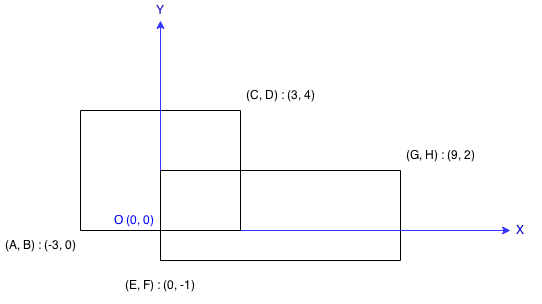
Assume that the total area is never beyond the maximum possible value of int.
44.Rectangle Area-Analysis
计算两个矩形的重叠面积
这个也很简单,找到重叠部分,然后计算面积就ok了
主要是复杂
第一个完全重合的情况
第二个相离得情况
第三个部分相交的情况
不同情况都要不同的结果
44.Rectangle Area-Solution-C/C++
int computeArea(int A, int B, int C, int D, int E, int F, int G, int H)
{
int a=0,b=0,c=0,d=0;
//完全重合情况
if(E<=A&&F<=B&&C<=G&&D<=H)
return (G-E)*(H-F);
if(A<=E&&B<=F&&G<=C&&H<=D)
return (C-A)*(D-B);
//不相交情况
if(C<=E||G<=A||D<=F||H<=B)
return (C-A)*(D-B)+(G-E)*(H-F);
//相交情况
a=A<E?E:A;
b=B>F?B:F;
c=C>G?G:C;
d=D<H?D:H;
int chang=(a-c)>0?a-c:c-a;
int kuan=(b-d)>0?b-d:d-b;
return (C-A)*(D-B)+(G-E)*(H-F)-chang*kuan;
}
后来补上的一个简单一些的方法
int max(int A,int E)
{
return A>E?A:E;
}
int min(int A,int E)
{
return A>E?E:A;
}
int computeArea(int A, int B, int C, int D, int E, int F, int G, int H)
{
int res = (D - B) * (C - A) + (H - F) * (G - E);
int A1 = max(A, E), B1 = max(B, F), C1 = min(C, G), D1 = min(D, H);
if (D1 <= B1 || C1 <= A1) return res;
return res - (D1 - B1) * (C1 - A1);
}
44.Rectangle Area-Solution-Python
貌似上面的我想复杂了,只需要用两个矩形的总面积-重复面积=全面积
完全不用单独列出来重合不重合的问题
class Solution(object):
def computeArea(self, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H):
"""
:type A: int
:type B: int
:type C: int
:type D: int
:type E: int
:type F: int
:type G: int
:type H: int
:rtype: int
"""
a=max(A,E)
b=max(B,F)
c=min(C,G)
d=min(D,H)
print(a,b,c,d)
chang=max(a-c,c-a)
kuan=max(b-d,d-b)
#按道理来说ab是左下的 cd是右上的
#也就是说ab的值应该小于cd的
#如果出现了ab值大于cd 就是相离的情况下会出现这种情况,那么就可以判断出来是否有重合部分了
if(d<b or c<a):
return (C-A)*(D-B)+(G-E)*(H-F)
return (C-A)*(D-B)+(G-E)*(H-F)-chang*kuan
Quote
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/zMn2ei
http://bookshadow.com/weblog/2015/05/29/leetcode-contains-duplicate-ii/